The Origin and Evolution of Life on Earth I
Charles Marshall, UC Berkeley
Evolutionary Biology Boot Camp
Charles Marshall, UC Berkeley
Evolutionary Biology Boot Camp
Douglas Erwin, Professor, Santa Fe Institute
July 12, 2006
During the greatest biodiversity crisis in the history of life some 250 million years ago, over 90% of all the species in the oceans died off in just a few hundred thousand years. Douglas Erwin, author of the new book Extinction: How Life on Earth Nearly Ended 250 Million Years Ago discusses his research in China, South Africa and the western US in search of the causes and consequences of this great mass extinction.
The Permian–Triassic extinction event, informally known as the Great Dying, was an extinction event that occurred 252 million years ago, forming the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as well as the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras. It is the Earth’s most severe known extinction event, with up to 96% of all marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species becoming extinct. It is the only known mass extinction of insects. Some 57% of all families and 83% of all genera became extinct. Because so much biodiversity was lost, the recovery of life on Earth took significantly longer than after any other extinction event, possibly up to 10 million years.
Researchers have variously suggested that there were from one to three distinct pulses, or phases, of extinction. There are several proposed mechanisms for the extinctions; the earlier phase was likely due to gradual environmental change, while the latter phase has been argued to be due to a catastrophic event. Suggested mechanisms for the latter include large or multiple impact events, increased volcanism, coal/gas fires and explosions from the Siberian Traps, and sudden release of methane from the sea floor; gradual changes include sea-level change, increasing aridity, and a shift in ocean circulation driven by climate change.
Surface conditions of the planets Venus and Mars are compared with those of Earth, and scenes of Earth’s living landscapes lead into a discussion of how unique Earth truly is. Major topics addressed in the series, including plate tectonics, natural resources, seismology, and erosion, are introduced in this program.
Early Greek astronomers believed that Earth was the center of the universe. However, this notion changed dramatically over time, especially after the invention of the telescope. This program traces the development of astronomical theory with discussions of the discoveries of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton. Unique characteristics of Earth are also discussed.
Oil wells do more than just produce oil — they serve as windows to Earth’s interior. This program introduces the topic of geophysics, exploring methods of studying what lies beneath Earth’s surface. Geophysicists use seismic wave studies, variations in temperature, magnetic fields, gravity, and computer simulations to create models of deep structures.
In the 1960s, earth scientists developed the theory of plate tectonics. This program traces the development of plate tectonics, beginning with the contributions and methods of geologist Alfred Wegener. Sea-floor spreading, continental drift, paleomagnetism, and the primordial supercontinent Pangaea are some of the topics covered.
This program examines the movement and interaction of tectonic plates, which account for a vast array of geologic formations and phenomena — from California’s San Andreas Fault to the Rift Valley of eastern Africa. The program covers convergent boundaries, subduction, hotspots, and the debate over what drives plate motion.
This program erodes the myth of the mountain as a solid, permanent structure. Animations are used to illustrate the process of orogeny (mountain building) through accretion and erosion, as well as the role of plate tectonics, the rock cycle, and how different types of rock are formed in the course of mountain building.
A visit to the Grand Canyon lays the foundation for this exploration of rock layers and deformation. The program covers sedimentation, major structures, the methods used to examine them, and how petroleum may be trapped inside them. It also looks at tectonic force and the different types of stress involved in the formation of geologic structures.
Showing actual footage of earthquakes and their aftermath, this program discusses the forces that fuel these massive events. Faults, waves, and the transfer of energy from the epicenter are explained, and histories of the seismograph and Richter scale are presented. The program also describes devices being developed to study — and eventually predict — earthquakes.
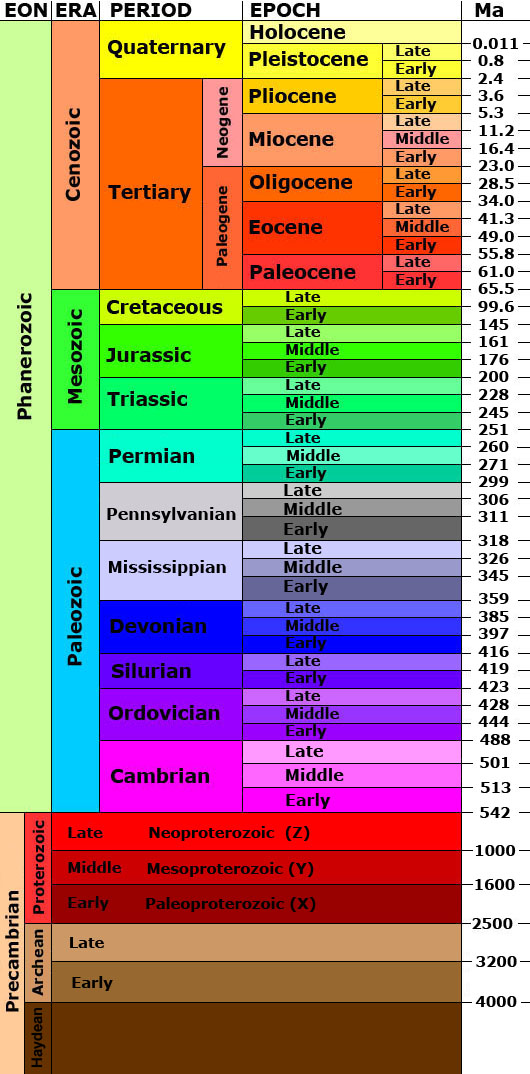
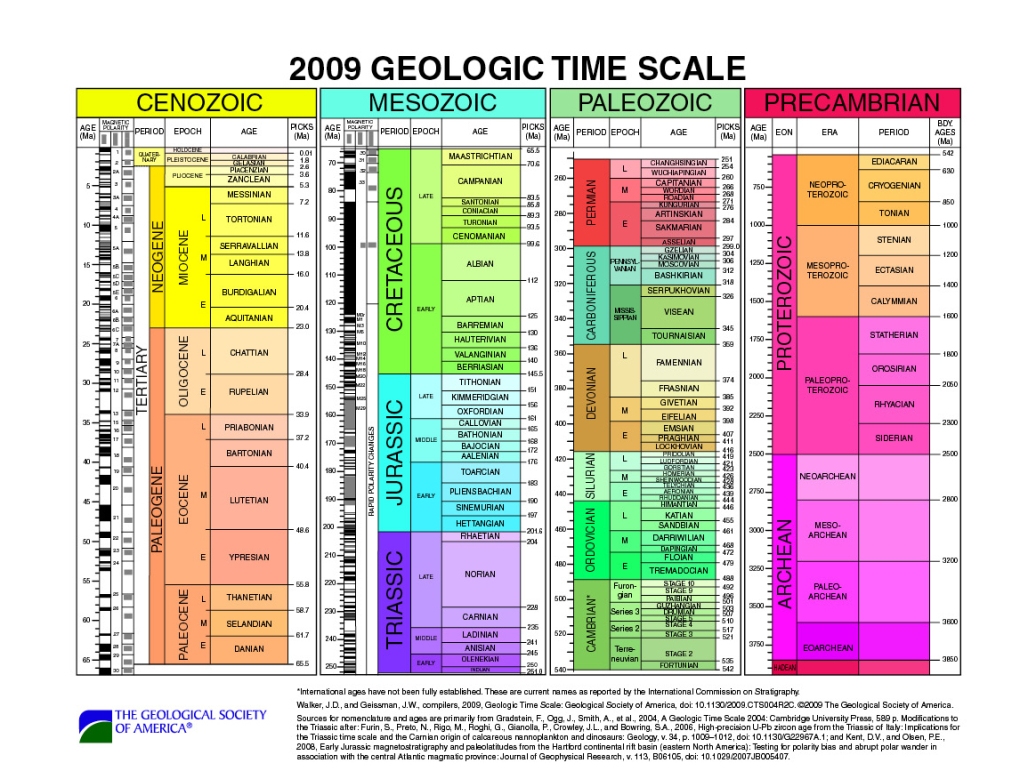
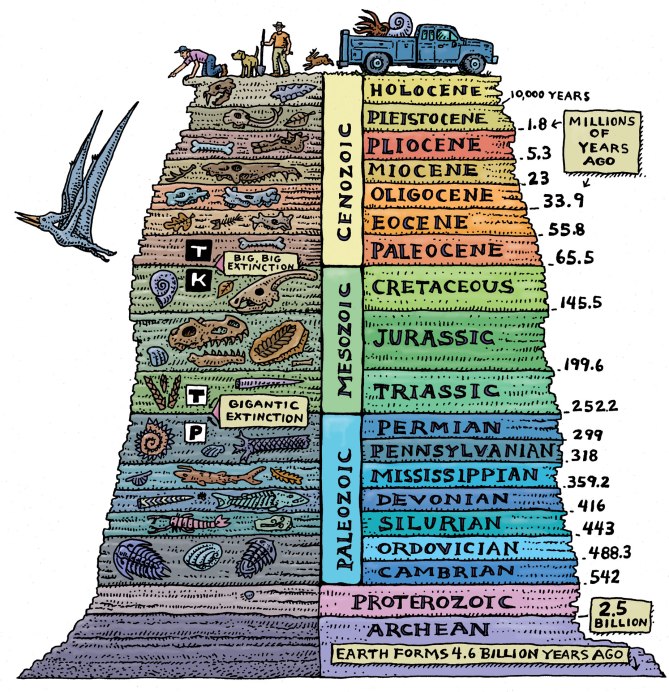
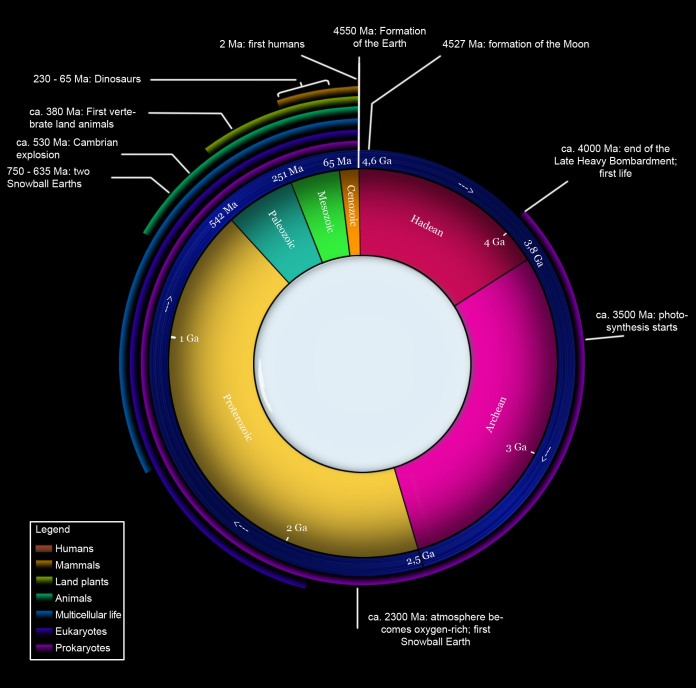
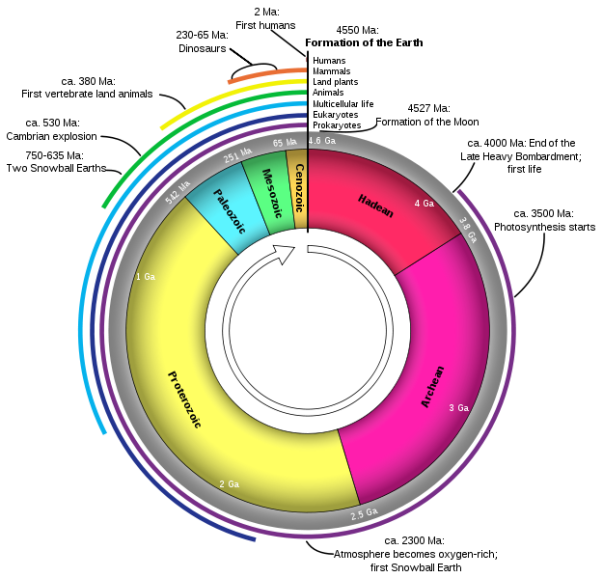
To illustrate the immensity of geologic time, the entire span of Earth’s existence is compressed down to a year. The timeline of major geologic events is superimposed onto the year for a condensed view of Earth’s evolution. A relationship between this timeline and that of life on Earth is established, with fossils and radiocarbon dating playing a major role in the discovery.
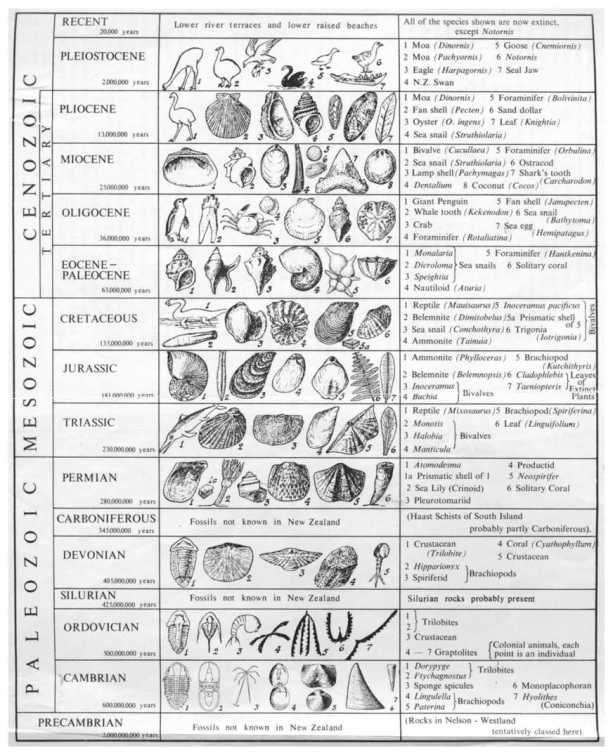
The fossil record reveals much about the diversity and development of species. This program examines the traces left by early plants, animals, and single-celled organisms and follows the progression of life forms over time. Connections are drawn between atmospheric gases, climate change, rock formation, biological functions, and mass extinctions.
Minerals have been indispensable to human civilization. This program looks at the variety of minerals, their atomic and crystalline structures, and their physical properties such as hardness and luster. Petrologists’ methods of sectioning rocks are shown, and gems, precious metals, ore excavation, and the value of silicates are discussed.
Volcanoes provide clues about what is going on inside Earth. Animations illustrate volcanic processes and how plate boundaries are related to volcanism. The program also surveys the various types of eruptions, craters, cones and vents, lava domes, magma, and volcanic rock. The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens serves as one example.
Most magma does not extrude onto Earth’s surface but cools slowly deep inside Earth. This magma seeps into crevices in existing rock to form intrusive igneous rocks. Experts provide a graphic illustration of this process and explain the types and textures of rocks such as granite, obsidian, and quartz. Once again, plate tectonics is shown to be involved in the process.
The Cleopatra’s Needle obelisk in New York City’s Central Park is severely weathered after only 75 years, whereas the dry climate of Egypt has preserved similar structures in that country for millennia. This program shows how weather, climate, chemicals, temperature, and type of substrate factor into rock and soil erosion. Environmental connections are also considered.
Anyone undertaking a building project must understand mass wasting — the downslope movement of earth under the influence of gravity. Various factors in mass wasting, including the rock’s effective strength and pore spaces, are discussed, as are different types of mass wasting such as creep, slump, and landslides. Images of an actual landslide illustrate the phenomenon.
This program returns to the Grand Canyon: its exposed layers of sedimentary rock allow scientists to peer into the geologic past. The movement of sediment and its deposition are covered, and the processes of lithification, compaction, and cementation that produce sedimentary rocks are explained. Organic components of rock are also discussed.
The weight of a mountain creates enough pressure to recrystallize rock, thus creating metamorphic rocks. This program outlines the recrystallization process and the types of rock it can create — from claystone and slate to schist and garnet-bearing gneiss. The relationship of metamorphic rock to plate tectonics is also covered.
Rivers are the most common land feature on Earth and play a vital role in the sculpting of land. This program shows landscapes formed by rivers, the various types of rivers, the basic parts of a river, and how characteristics of rivers — their slope, channel, and discharge — erode and build the surrounding terrain. Aspects of flooding are also discussed.
The Colorado River is a powerful geologic agent — powerful enough to have carved the Grand Canyon. This program focuses on how such carving takes place over time, looking at erosion and deposition processes as they relate to river characteristics and type of rock. The evolution of rivers is covered, along with efforts to prevent harmful consequences to humans.
Approximately three-quarters of Earth’s surface is covered by water. But most fresh water comes from underground. Topics of this program include aquifers, rock porosity and permeability, artesian wells, the water table, cave formation, sinkholes, and how groundwater may become contaminated.
Land in arid climates is shaped in particular ways. This program shows how deserts are defined by infrequent precipitation and how desertification relates to proximity to the equator, proximity to mountains, and ultimately plate tectonics. Images of landscapes illustrate how wind creates features such as dunes, playas, blow-outs, and even oases.
Many of the world’s most beautiful landscapes were made by glaciers. This program shows how, explaining glacial formation, structure, movement, and methods of gouging and accumulating earth. The program provides images of glaciers and glacial landforms such as moraines, and discusses how study of glaciers may help us understand ice ages and the greenhouse effect.